The Need for Federal Investment in Cell-Based Therapies for Patients with COVID-19, September 2021
A new report released by Alliance for Cell Therapy Now, an independent, non-profit organization guided by leaders representing academic and medical institutions, industry innovators, and patients, describes the number of clinical studies that explore the use of cell-based therapies for patients with COVID-19 and the urgent need for federal funding to support the development, and ultimately, the manufacturing of these therapies to support patients in need. As Congress considers appropriations for the coming year, it should designate funds for research on cell-based therapies to augment limited options currently available, to help seriously ill patients with COVID-19, as well as those with other serious and life-threatening conditions.
Executive Summary
As the nation continues to face the unprecedented and growing challenges of the coronavirus pandemic, the number of Americans that are contracting COVID-19, becoming hospitalized, and in many cases—dying—is high and continuing to grow. More than 40 million Americans have tested positive for COVID-19 and more than 650,000 Americans have died. The combination of the now predominant Delta variant—which is far more contagious and causes more severe illness—and the
fact that more than 45% of the American population still remains unvaccinated, is driving surges in hospitalization across the country, with many hospitals now canceling elective surgeries to make room for COVID-19 patients.
Click here to access the report
There is an urgent need for new treatments to help reduce the severity of illness, the number of hospitalizations, and death related to COVID-19. Evidence from numerous clinical studies shows that cell-based therapies can play a key role in helping severely ill patients with COVID-19, given their immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory characteristics.
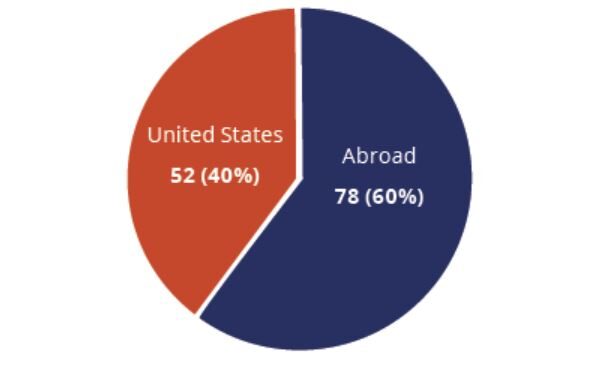
At least 130 clinical studies have been launched that explore the use of cell-based therapies for patients with COVID-19, 52 (or 40%) of which are being conducted in the United States. At least 175 peer-reviewed articles have been published that describe the promise or potential of these therapies for treating COVID-19 patients. One recent meta-analysis and systematic review led by researchers at the Mayo Clinic in collaboration with several other academic leaders showed that MSC cell administration to hospitalized patients with COVID-19 was associated with a 69% reduction in all-cause mortality risk and a 64% reduction in severe adverse events.
While results from clinical studies are promising, the vast majority of such studies (89%) are either Phase 1 or Phase 2 studies. Large-scale, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials are needed to confirm early results and help bring safe and effective treatments to patients in need.
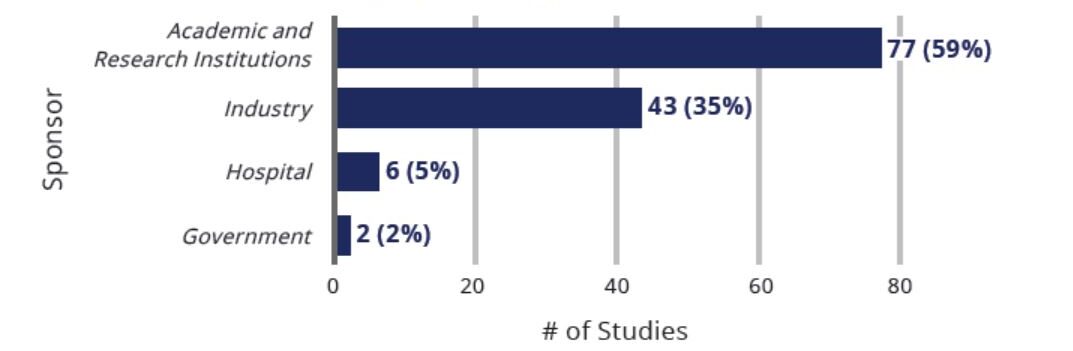
The largest barrier to conducting clinical research related to cell-based therapies is the high cost of conducting these studies. The financial barriers associated with clinical trials are particularly problematic for academic and research institutions and small biotechnology companies, who are responsible for nearly all of the clinical trials being conducted for COVID-19 both in the U.S. and abroad. Federal funding is needed to help bring promising cell-based therapies to patients with COVID-19 and other serious and life-threatening conditions.
The Administration recognizes the lack of reliable and accessible treatments for COVID-19 and the need for investment in the development and manufacturing of therapies. Both the January 21, 2021 Executive Order and the American Rescue Plan (which formed the basis for the COVID-19 relief package passed by Congress and signed into law in March 2021) contained policies to accelerate the development of novel therapies to treat COVID-19. In early September 2021, the Administration released a COVID-19 action plan that also contained actions that support the development and administration of treatments to reduce hospitalizations and save lives.
Congress authorized nearly $40 billion in funding for vaccines, therapeutics, and other medical supplies within three COVID-19 relief packages—two of which were passed and signed into law in 2020 and one of which was signed into law in early 2021, but none of such funding was directed towards the development of cell-based therapies for patients with COVID-19.
Several Democratic and Republican members of the House of Representatives and the Senate have called for greater investment in the development and manufacturing of cell-based therapies to support patients in need. As Congress considers appropriations for the coming year, as well as a reconciliation package this Fall, it should designate funds for research on cell-based therapies to augment limited options currently available, to help seriously ill patients with COVID-19, as well as patients with other serious and life-threatening conditions.
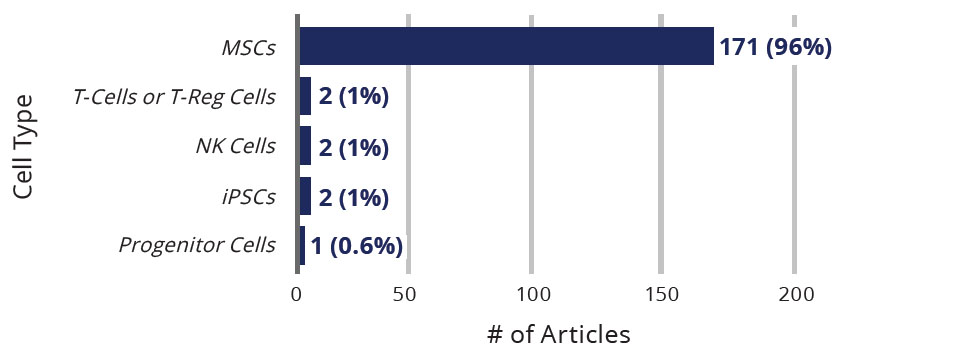
At least 178 review articles have been published in peer-reviewed publications offering insights on the potential or promise of cell-based therapies for patients with COVID-19. The vast majority (171 or 96%) of such review articles describe the role of MSCs in treating COVID-19 patients.
Clinical Studies Exploring Use Of Cell-Based Therapies for COVID-19 By Location (n=130)
All Clinical Studies Exploring Use of Cell Based Therapies For COVID-19 By Phase (n=130)
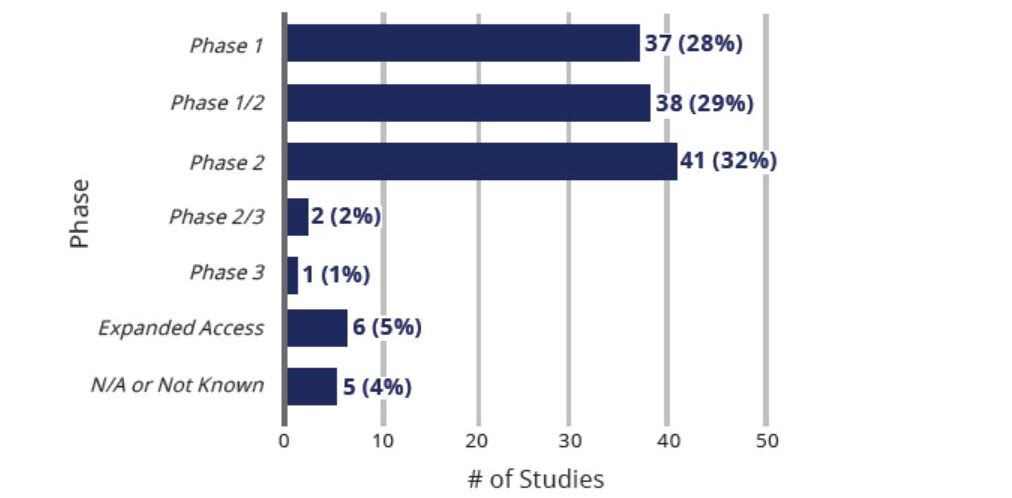
The vast majority of studies (89%) are either Phase 1 (28%), Phase 2 (29%), or Phase 1/2 (32%) clinical trials.
Two of the studies are Phase 2/3 clinical trials and only one is a Phase 3 clinical trial.
There are 6 expanded access studies and the phase is not known or applicable for the remaining 5 studies.
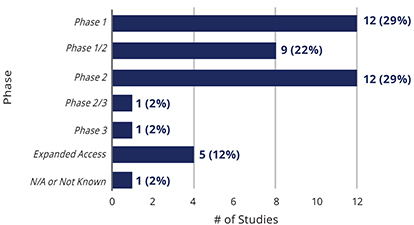
U.S. Clinical Studies Exploring Use of Cell-Based Therapies for COVID-19 By Phase (n=41)
Clinical Studies Exploring Use Of Cell-Based Therapies for COVID-19 By Sponsor Type (n=130)
Clinical Studies Exploring Use Of Cell-Based Therapies for COVID-19 By Cell Type (n=130)
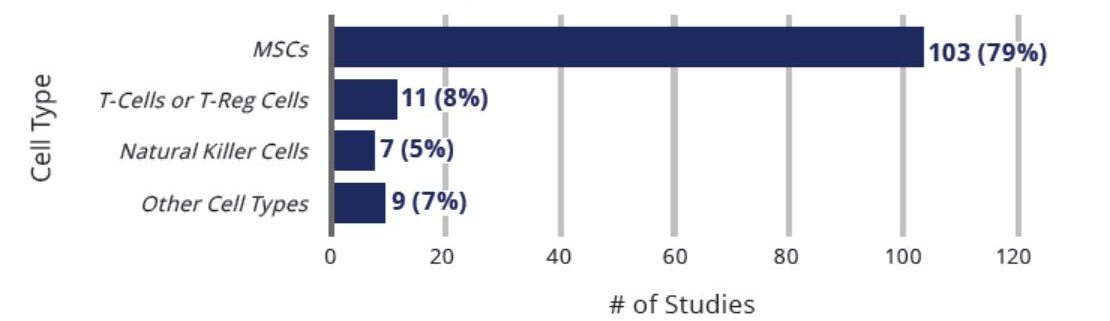
The vast majority (103 or 79%) of the 130 studies conducted globally are focused on the use of MSCs for patients with COVID-19. Other cell-based therapies are being explored, including T-cells and T-Reg cells, NK cells, and other cells.